Why protecting your data has never mattered more
In today’s hyper-connected, data-driven world, security isn’t just an IT issue, it’s a critical business imperative. Every organization, regardless of industry or size, relies on sensitive information to operate, innovate and compete. Yet, the risks of data loss, exposure or misuse have never been higher. Regulatory pressures, like GDPR and CCPA, impose strict requirements with significant financial and reputational consequences. A single data breach can disrupt business, erode stakeholder trust and leave a lasting mark on your brand’s reputation.
Despite heavy investments in security tools, many organizations still struggle with real gaps. Too often, data security is approached as a series of disconnected checkboxes, rather than a unified, proactive program. The difference between checking the box and real protection is the difference between compliance and confidence.
To earn the trust of leadership, auditors and customers, your organization needs a holistic strategy that:
That’s why we created this guide. Leading security today means navigating a landscape full of uncertainty, shifting regulations and rising expectations. Whether your data program is mature or just starting out, you’re likely facing challenges that aren’t always obvious, or easy to solve alone. This guide was created to serve as a practical resource. Here, you’ll find a framework for evaluating your current approach, uncovering blind spots and gaining clarity on what truly matters most. The path forward isn’t just about more technology or more policies, it’s about connecting the dots, building confidence at every level and giving your organization the peace of mind it needs to move forward securely.
The three pillars of data security: Privacy, governance and security
Building an effective data security program starts with the three pillars that support and shape every resilient strategy; privacy, governance and security. These aren’t buzzwords or siloed functions, they are deeply interconnected domains that, when managed together, turn scattered tools and policies into a program that can stand up to both today’s risks and tomorrow’s unknowns.

When these pillars operate independently, gaps inevitably form. Most organizations, eager to protect themselves, over-invest in security technologies without first establishing the policies, processes and visibility that true resilience demands. The result? A fragmented approach that struggles to keep pace with regulatory changes, business transformation and the ever-growing volume of data.
True resilience requires all three pillars working together, reinforcing each other. Privacy gives you the mandate and focus. Governance brings structure and oversight. Security delivers the technical enforcement and operational muscle. When aligned, these pillars transform data security from a cost center into a business enabler, protecting what matters most, building stakeholder trust and supporting innovation without fear.
Imagine your data security program as a structure: privacy, governance and security are the columns that support everything above. Take away one, and the structure is unstable. Invest equally, and you create a platform strong enough to weather audits, breaches and evolving threats.
Key takeaway
True data security isn’t just about technology or compliance, it’s about balance. When privacy, governance and security work in concert, your program becomes adaptable, resilient and ready for whatever comes next. Overlook one pillar, and you risk costly gaps. Strengthen all three, and you build lasting trust and business value.
In the following sections, we’ll show how to bring these pillars into balance, moving beyond checkboxes and tool sprawl to a program that truly protects and empowers your organization.
Administrative & Technical controls: Why you need both
What makes a data security program truly effective isn’t just what you write down in a policy or how impressive your tech stack looks, it’s how well your organization connects its intentions with real-world actions. That connection depends on a thoughtful balance between two core categories: administrative controls and technical controls. Understanding the difference, and why you need both, is at the heart of any program that delivers more than just “check the box” compliance.
Administrative controls: The foundation for accountability
Administrative controls are the written rules, policies and defined processes that provide a strategic foundation for data security. These controls answer critical questions: What does our organization believe about data security? Who is responsible for what? What should people do when faced with a potential risk.
They typically include:

Administrative controls often form the backbone of compliance. Auditors and regulators look for them because they provide visible proof that your organization is thinking carefully about how it manages risk. They help drive culture, clarify accountability and reduce ambiguity. However, policies alone rarely stop a breach or prevent accidental exposure. As any security leader knows, a policy is only as good as its adoption, but that can lag without the right support and oversight.
Technical controls: Turning policy into practice
Technical controls are the technologies and automated mechanisms that enforce the standards set by your administrative controls. These are the systems and tools that do the heavy lifting, operating behind the scenes to keep your environment safe even as your business evolves. Technical controls make policies real by providing continuous, consistent enforcement.
They include:

Technical controls bring your policies to life, filling the gaps that human error and manual processes can’t address at scale. With modern organizations managing data across SaaS apps and GenAI apps, on-premise file shares, endpoints, emails and more, only technical controls can enforce standards consistently, without slowing business down.
How the two work together
Consider this example: Your organization’s policy requires that all personal identifiable information (PII) be encrypted at rest. That’s an administrative control. But unless you deploy a technical control, like automated DLP and encryption solutions, there’s no guarantee the policy is actually being followed. Manual enforcement is rarely enough, especially as data volumes grow and environments change. Without technical controls, policies become “shelfware," impressive in an audit binder but ineffective in practice.
On the other hand, technical controls without administrative clarity can create confusion or conflict. Tools must be configured, monitored and managed with a clear understanding of business objectives and legal requirements. Otherwise, they risk creating friction, introducing complexity or even blocking legitimate business activity. The best programs use administrative controls to set the vision and technical controls to operationalize it.
Within a company, various distinct business units hold a stake in the shared responsibility model for data security. This delineates security obligations between different internal teams with the goal of holistic data security, governance and compliance.
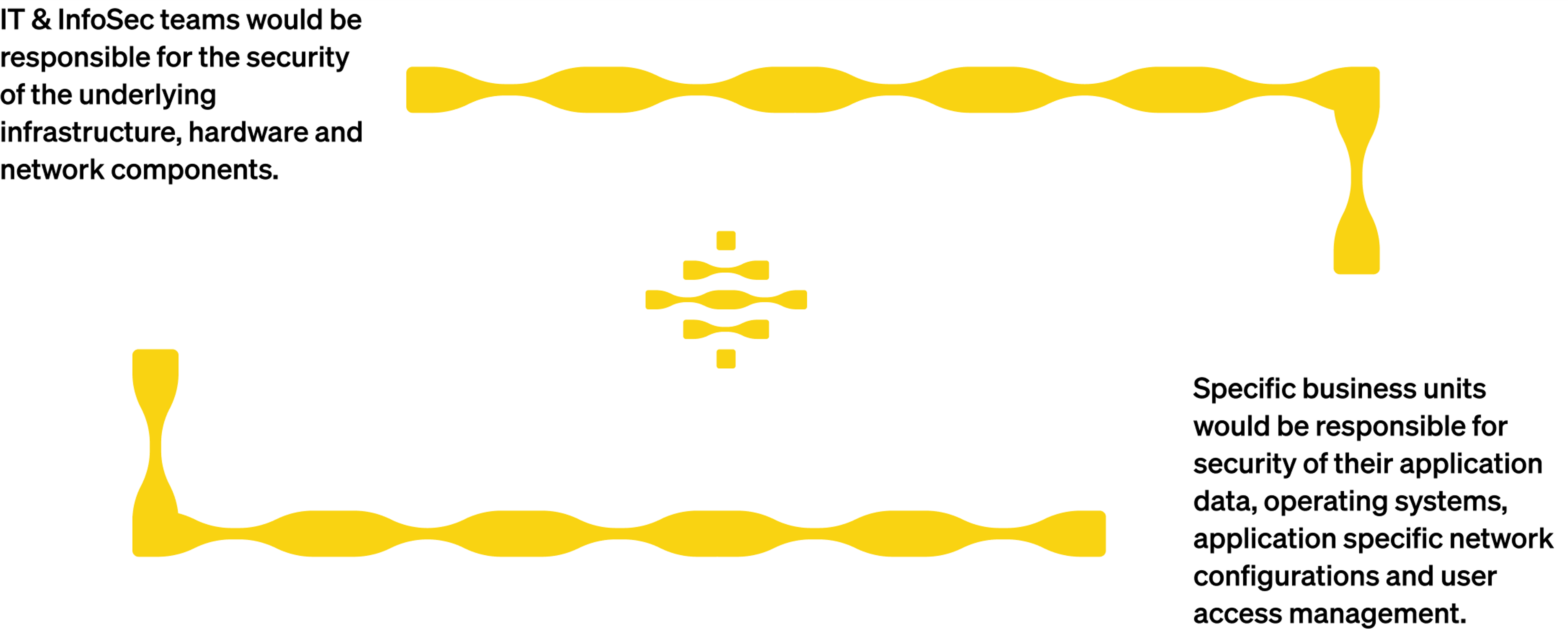
This partnership allows the business to maintain control over their most critical assets, optimizing resources and improving overall data protection.
Why both matter
It’s common to see organizations invest heavily in one category and under-invest in the other. Sometimes, businesses create beautifully written policies that sit idle because no one builds the workflows or invests in automation. Other times, organizations deploy the latest tools but fail to document why or how those tools should be used, leaving employees uncertain and unprepared. At worst, some organizations lack the defined shared responsibility model to use different technologies together which leads to enormous gaps in both administrative and technical controls.
The reality is that lasting data security comes from the synergy of both categories. Administrative controls give everyone clarity and set expectations. Technical controls quietly, reliably enforce those expectations, around the clock and at scale.
Key takeaways
- Lasting data security only happens when policies and technology work hand-in-hand. Administrative controls set clear expectations and accountability, while technical controls turn those expectations into everyday practice. Invest in both and connect them through automation so you can build a program that’s truly effective, adaptable and trusted.
- If you want your data security program to do more than pass an audit, start by reviewing your administrative controls. Are your policies up to date, actionable and clearly assigned? Next, examine your technical controls. Do they truly support your policies, or are there gaps between what you say and what you do? The most resilient programs regularly review both sides, continually tuning policies to meet changing business and regulatory requirements and updating technology to reflect evolving risks.
- By investing equally in administrative and technical controls, and connecting them through clear processes and automation, you lay the groundwork for a security posture that is proactive, adaptable and trustworthy. This balance not only helps you avoid gaps and audit findings; it frees your team to focus on what matters most: protecting your business, your people and your reputation.
Understanding frameworks, standards and controls
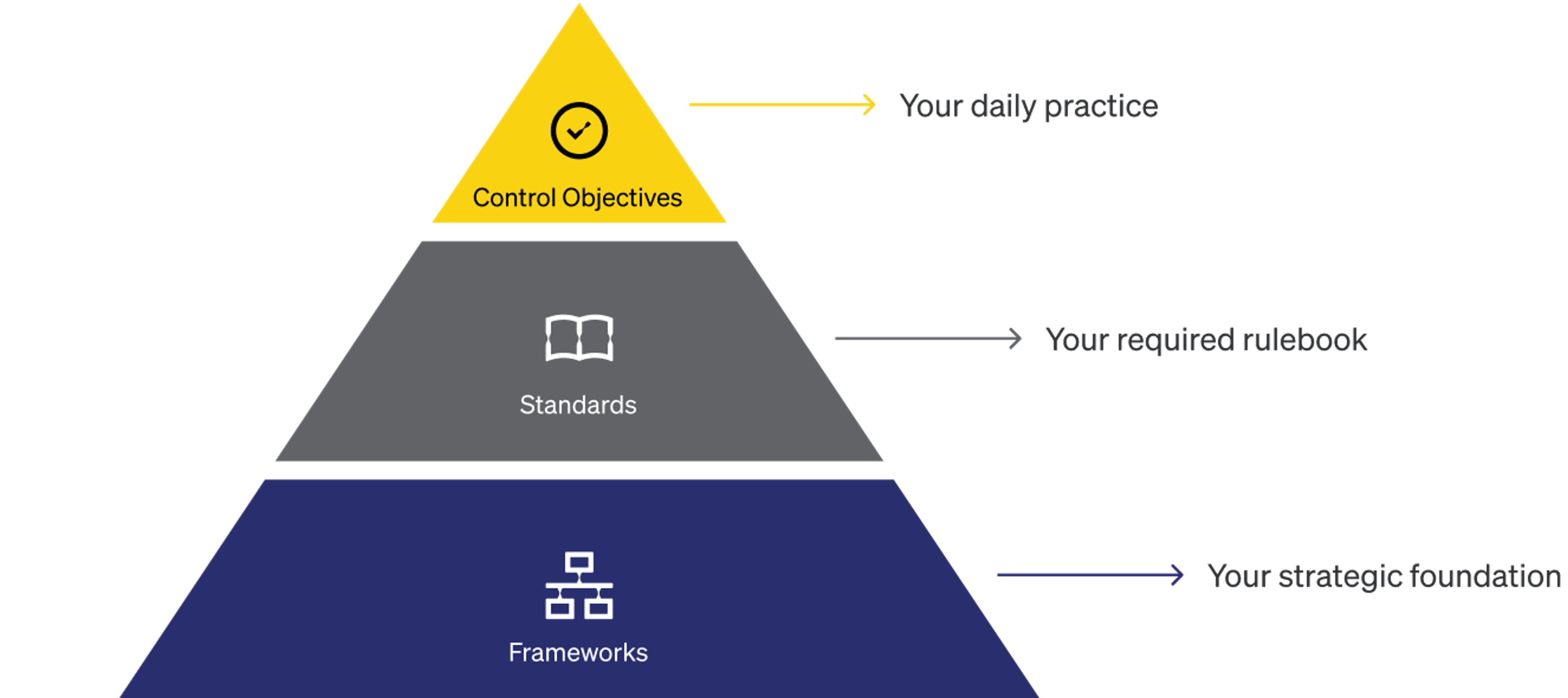
No two organizations face the same data security challenges, but all benefit from a clear structure that translates strategy into action. The most effective programs start with a proven framework, apply relevant standards and bring them to life with actionable controls. Together, these elements ensure your data security program is built on best practices, is auditable and is adaptable as regulations and risks evolve.
Frameworks: The strategic foundation
Frameworks provide the overall blueprint for your security program, offering structured guidance on how to manage risk and prioritize actions.
Well-known frameworks include:
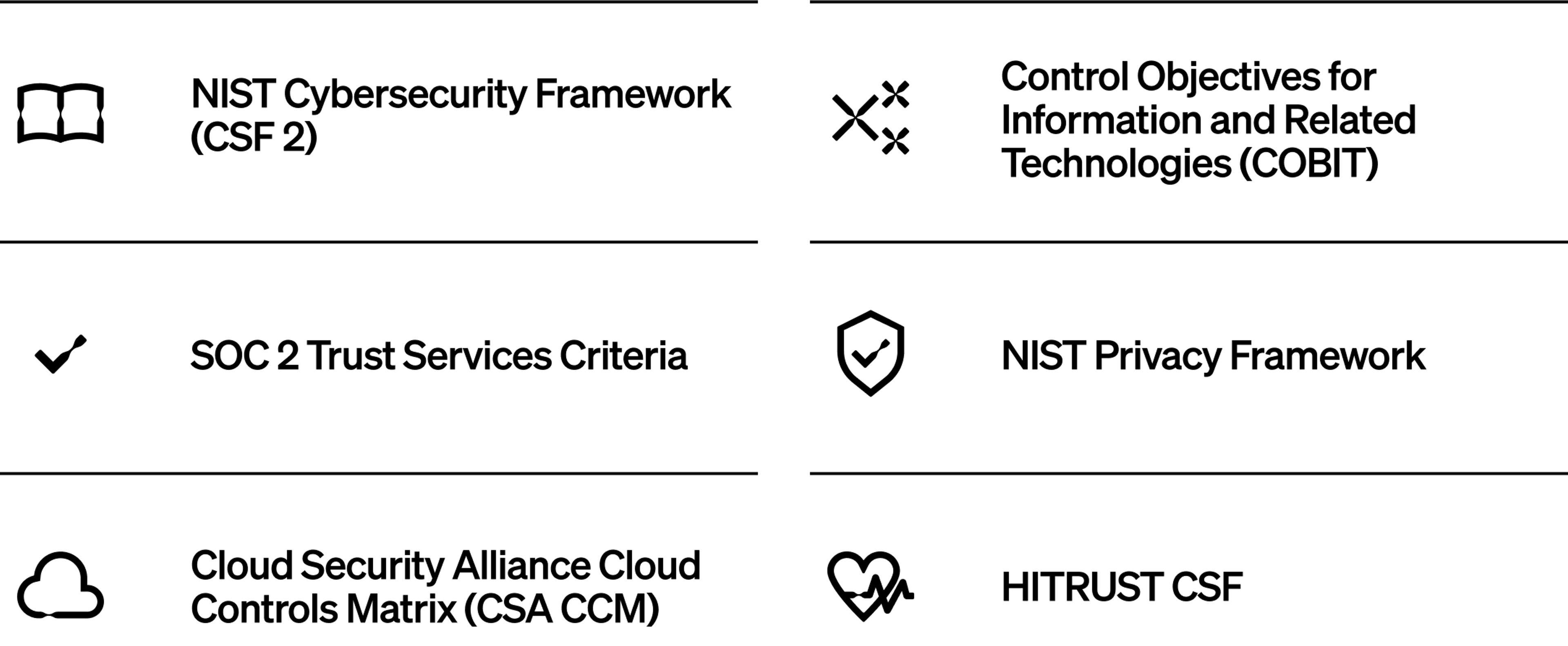
Frameworks define your program’s why and give some direction on what to do, from asset identification and risk assessment to monitoring and recovery. They offer a shared language for your teams, your board and auditors.
Standards: The rulebook for compliance
Standards translate broad frameworks into specific, auditable requirements. Some are regulatory (required by law), while others are industry best practices or customer-driven.
Key standards include:
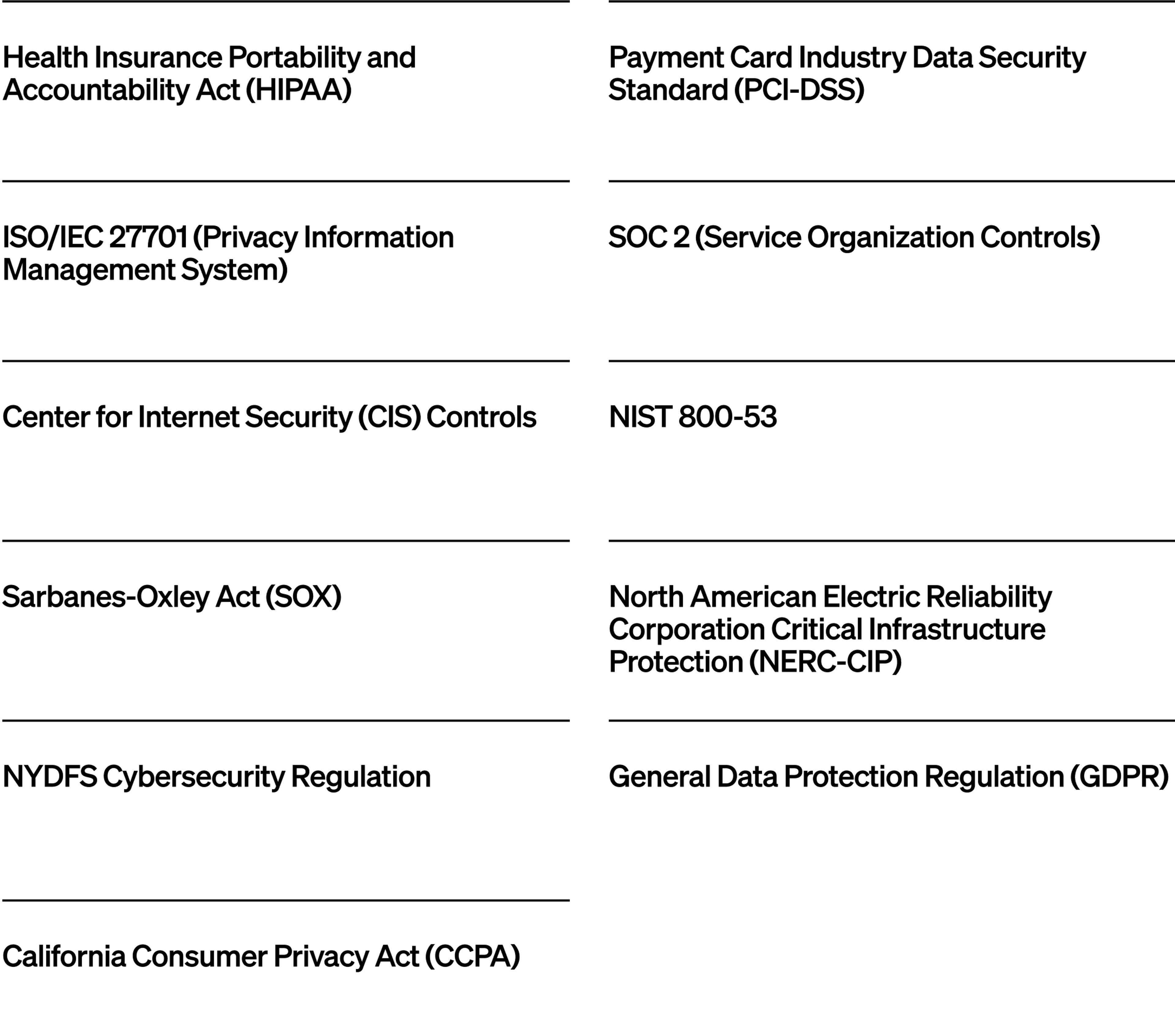
These standards spell out what you must do: encrypt certain data, limit access, retain audit logs, provide breach notifications and more. They often reference controls, specific steps and technologies to be implemented.
Controls and control objectives: Bridging policy and practice
Controls are the concrete actions, technical solutions and processes you implement to fulfill standards. Controls are often defined by frameworks or standards themselves, and should be mapped to your environment.

Each control or objective is a practical step, turning frameworks and standards from theory into day-to-day operational reality.
Key Takeaway
A mature data security program connects vision to reality: start with a robust framework, implement the right standards and operationalize them with clear controls. This approach not only helps you meet compliance but also builds resilience, simplifies audits and prepares your organization to confidently adapt as threats and regulations evolve.
How it all fits together: A visual model
This structure ensures alignment from boardroom vision to frontline activity. When auditors or regulators review your program, they’ll want to see this mapping in action.
Real-world example
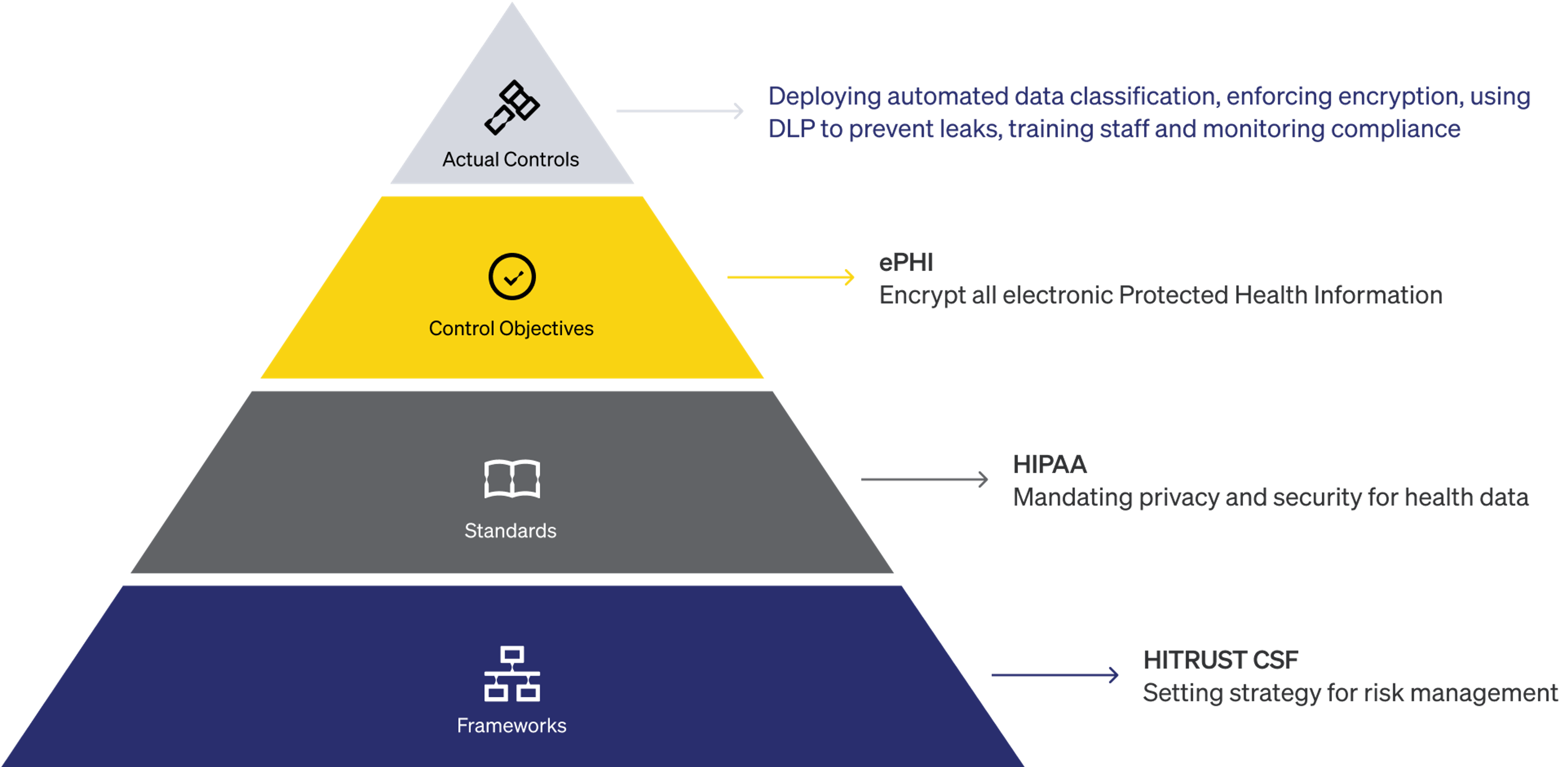
Doing these things allows organizations to properly track data security maturity and growth.
Key takeaway
A mature data security program connects vision to reality: start with a robust framework, implement the right standards and operationalize them with clear controls. This approach not only helps you meet compliance but also builds resilience, simplifies audits and prepares your organization to confidently adapt as threats and regulations evolve.
The role of automation in modern data security
For most organizations, the promise of a strong data security program often collides with the hard reality of manual work. Security and compliance teams find themselves drowning in repetitive, time-consuming tasks: manually classifying sensitive information (or asking end-users to), chasing down every alert, documenting and remediating incidents, updating policies and preparing for the next audit. Even with solid policies and the best of intentions, manual processes can grind momentum to a halt and leave dangerous gaps for risk and error.
The pain of manual data security
Manual data classification is a prime example. In theory, organizations know the importance of labeling and tracking sensitive data. In practice, classification is often left to end-users, an approach that is inconsistent at best, and sometimes ignored entirely. When security depends on human vigilance, important data can slip through the cracks, go undiscovered or end up in places it doesn’t belong. As data grows in volume and velocity, the task becomes unmanageable.
Alert management is another pain point. Traditional DLP systems and monitoring tools generate thousands of alerts each day. Many of these turn out to be false positives or low risk, but every one requires review. The result is alert fatigue, teams become numb to the noise, increasing the risk that true threats are missed entirely. Over time, this endless triage can erode morale and leave security teams in a constant state of reaction, never getting ahead.
Compliance adds another layer of complexity. Regulations change, audits become more frequent and documentation requirements get more rigorous. Without automation, compliance becomes a resource drain: updating spreadsheets, tracking access and responding to auditor requests can swallow hours of staff time, time that could be spent proactively improving your security posture.
Why manual approaches fall short
Manual security operations don’t scale. As organizations grow, so does the amount of data to protect. New SaaS apps, GenAI tools and remote endpoints multiply the places where data lives and moves. Human-driven processes simply can’t keep up with this pace, leading to bottlenecks, oversight gaps and an ever-present risk of non-compliance.
There’s also the reality of human error. Even your best people can make mistakes when they’re overwhelmed, bored or under pressure. Manual handling increases the odds that sensitive data is misclassified, alerts are ignored or compliance obligations are missed. These lapses, often invisible until it’s too late, can have devastating consequences for the business.
The shift toward automation
Organizations everywhere are recognizing the need to move away from manual data security and toward automation. Automation, powered by intelligent rules and AI, transforms how you approach key security and compliance tasks:

The possibilities of autonomous DLP
With the emergence of autonomous DLP, organizations are seeing the power of moving from manual intervention to intelligent, automated security. Instead of relying on end users or overwhelmed analysts to spot problems, autonomous DLP systems can:

This new level of automation enables organizations to move from reactive, manual firefighting to proactive, scalable security management. Data security becomes less about chasing problems and more about preventing them, freeing up valuable time and attention for higher-level work.
Why automation matters for everyone

Key Takeaway
As you assess your own data security program, consider where manual work is causing bottlenecks or risk. Start by automating the most time-consuming or error-prone tasks, such as data discovery, alert management or compliance tracking. From there, explore how autonomous DLP and intelligent automation can deliver deeper visibility, stronger protection and a more sustainable workload for your team.
The future of data security belongs to organizations that embrace automation, not as a replacement for human expertise, but as a way to extend it, amplify it and focus it where it matters most.
Data security checklist: Is anything missing in your current program?
Use this checklist to assess your organization’s current state across the critical pillars.
Governance & program management
- Is there a documented, up-to-date data governance framework with clearly defined roles and responsibilities?
- Have all data assets (structured, unstructured, SaaS, endpoint, file shares,) been inventoried and classified?
- Are data ownership and stewardship responsibilities assigned, reviewed and communicated to stakeholders?
- Are data collection, storage, processing, sharing and disposal workflows mapped and updated regularly?
- Is there a steering committee or governance body overseeing the data program?
- Are governance policies and procedures reviewed and improved at least annually?
- Are escalation and decision-making paths clear for data-related issues or incidents?
Risk management
- Has a formal data risk assessment been performed within the last 12 months?
- Is there a repeatable process for identifying, assessing and prioritizing data security risks?
- Is the risk register current, with owners and due dates for remediation?
- Are risk mitigation actions documented, tracked and reviewed by leadership?
- Are emerging risks (AI, new SaaS apps, remote work) continuously identified and evaluated?
- Do we have visibility into third-party/vendor data risks?
Privacy & regulatory compliance
- Are we up-to-date on all currently applicable standards and regulations (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, etc.) for our markets and data types?
- Is there documented evidence of compliance and maturity for policies, procedures, audit logs and reports?
- Are processes in place to respond to timely data subject access requests (DSARs) (i.e. access, correction, deletion, portability)?
- Is privacy and data protection training conducted regularly for all employees?
- Are data privacy impact assessments (DPIA) performed for new systems, vendors and data uses?
- Are all vendor and partner contracts reviewed for data processing agreements and privacy clauses?
- Is there a defined process to log, report and respond to data security incidents per regulatory requirements?
Administrative controls
- Are all data security policies (classification, access, retention, incident response) documented, current and communicated?
- Is onboarding/offboarding for employees and vendors tightly controlled and audited?
- Are user permissions and access rights reviewed on a regular schedule?
- Are policy reviews and security awareness campaigns conducted at least annually?
- Is there a process for logging, reporting and escalating security or compliance issues?
- Are exception approvals tracked and periodically reviewed?
- Do managers have clear checklists for data-related responsibilities?
Technical controls
- Is automated data discovery and classification deployed for all critical data sources?
- Are DLP and monitoring solutions active for data at rest and in motion?
- Is strong encryption enforced for sensitive data, both at rest and in motion?
- Is MFA required for all privileged and remote access?
- Are endpoints (laptops, desktops, mobile, cloud VMs) protected with up-to-date security agents?
- Do we have automated alerting and response playbooks for critical incidents?
- Are backups encrypted, regularly tested and secured against ransomware?
Incident management & response
- Is there a written, tested incident response plan that addresses the most critical data security and privacy incidents?
- Are incident simulations, tabletop exercises or drills performed at least once per year?
- Is incident detection, escalation and notification time tracked and measured for improvement?
- Is there a defined cross-functional responsibility model for responding to and escalating data security incidents?
- Is post-incident review mandatory, with documented lessons learned and process changes?
- Are key contacts and communication plans up-to-date for regulatory and customer notification?
- Do we have a process for coordinating with legal, PR and executive teams during incidents?
- Are incidents logged and analyzed for root cause and recurring patterns?
Audit & continuous improvement
- Are internal and external audits performed regularly, with actionable findings and tracked remediation?
- Are compliance and risk postures monitored with automated tools or dashboards?
- Are control effectiveness metrics (i.e. KPIs) defined and measured over time?
- Do we benchmark our program against industry standards and update as needed?
- Are lessons learned from incidents and audits used to inform program updates?
- Is there a feedback loop for employees to report gaps, ideas or improvements?
- Are program updates and improvements communicated organization-wide?
Key Takeaway
This checklist is designed to show areas where you may be exposed to unnecessary risk, compliance failures or operational blind spots. Treat this checklist as a starting point, prioritize gaps and make data security governance, risk, compliance and security an ongoing, organization-wide effort.
The autonomous way to mind what matters
MIND was built to change the way organizations protect their most sensitive data, by putting intelligent automation at the core of data security. Unlike legacy approaches that rely on manual effort or rigid rules, MIND takes a fundamentally different approach: automatically understanding, classifying and securing data wherever it lives, whether at rest or in motion.
With MIND, your organization gains the power to continuously inventory data across GenAI and SaaS apps, on-premise file shares, endpoints and emails with no more blind spots or missed risks. Its AI-driven classification engine doesn’t just scan for patterns, it learns what matters most to your business, labeling and prioritizing sensitive data with context and accuracy. When data moves, whether it’s shared with a partner, accessed by a remote user or uploaded to a GenAI tool, MIND autonomously enforces policy, prevents risky behavior and ensures compliance, all without slowing down your teams or disrupting business as usual.
This isn’t just about efficiency. It’s about confidence. MIND’s approach reduces false positives, lightens the burden on your security team and provides real-time visibility and control across your entire environment. The result is a data security program that adapts as your business evolves, meeting regulatory demands, empowering innovation and freeing your team to focus on what truly matters. With MIND, data protection moves from a reactive struggle to an enabler of trust, resilience and business growth.